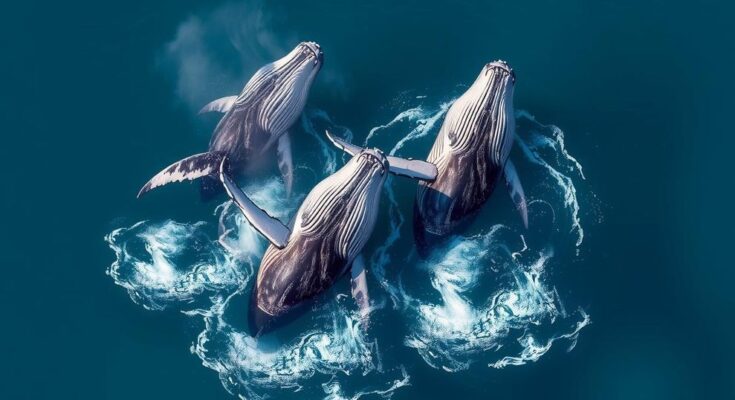
A humpback whale’s recent unusual migration from Colombia to Zanzibar raises concerns among scientists regarding environmental changes and their impacts on krill, the whale’s primary food source. Research suggests climate change may be a significant factor affecting whale behavior. Further studies aim to enhance conservation efforts and address the implications of shifting migration patterns on marine ecosystems.
Recent observations of a humpback whale have sparked concern among scientists due to its extensive deviation from the typical migration route. Notably sighted in Zanzibar after being first identified off the Colombian coast years earlier, researchers conducted a thorough investigation and documented their findings in the journal Royal Society Open Science. Lead researcher Dr. Ekaterina Kalashnikova noted that while the precise reasons for this unusual behavior remain unidentified, potential influences include climate change, extreme environmental occurrences, and evolutionary adaptations. Such deviations could represent critical adaptations for the species in response to environmental pressures, which merit further investigation.
The migration of humpback whales significantly correlates with their food sources, particularly krill. Research conducted by the University of Oregon indicates that environmental changes, notably warmer ocean temperatures, can adversely affect krill populations. Should this be the driving factor behind the whale’s unexpected long-distance travel, it could lead to food instability, ultimately threatening the survival of humpback whales as they may exhaust themselves in search of adequate resources. This scenario exemplifies how climate change can diminish biodiversity and disrupt ecosystem functionality.
Another hypothesis posited by the research team is that the migration may indicate recovering humpback populations due to successful conservation initiatives. However, this needs to be substantiated with further study. The findings from this research hold significant implications for future conservation strategies and climate change mitigation efforts. A deeper understanding of these migration patterns is essential for effectively planning marine protected areas and safeguarding marine ecosystems against the detrimental impacts of climate change.
While certain species may exhibit behavioral adaptations to cope with environmental changes, researchers emphasize the need to focus on reducing pollution that contributes to global warming. This effort is crucial for ensuring the long-term survival and well-being of numerous species.
Humpback whales are known for their remarkable migrations between tropical breeding grounds and colder feeding areas. Recent studies have highlighted shifts in these migration patterns, prompting researchers to closely monitor the causes behind such changes. The availability of krill, a primary food source, is significantly influenced by environmental conditions, including ocean temperature. Understanding these dynamics is vital for ensuring the sustainability of marine life amidst escalating climate threats.
The documented behavior of the humpback whale reveals a potential shift in migration patterns, driven by environmental factors such as climate change. This raises alarms regarding the stability of food sources for whale populations, which may lead to severe consequences for their survival. The research emphasizes the necessity for ongoing conservation efforts and a comprehensive understanding of marine ecosystem dynamics to mitigate the impacts of climate change and support biodiversity.
Original Source: www.thecooldown.com