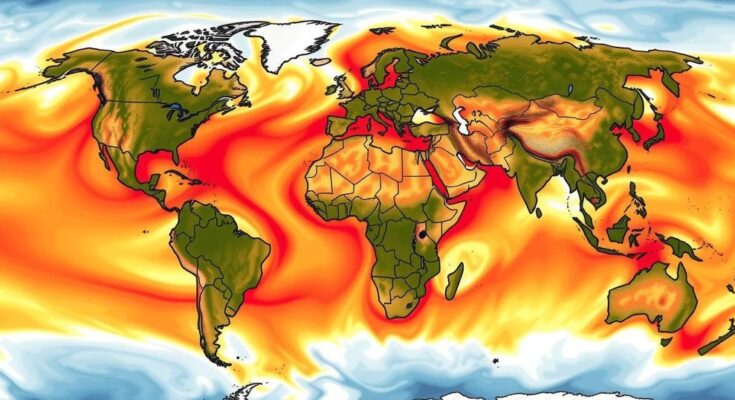
In 2024, global temperatures reached record highs, surpassing the 1.5C threshold for the first time, driven by fossil fuel consumption. This year marked the hottest on record, with extreme weather conditions affecting millions worldwide. Experts emphasize urgent action to reduce emissions and address the accelerating climate crisis, with potential catastrophic heating predicted if current practices are not reversed.
In 2024, the planet experienced its hottest year on record, with global average temperatures reaching 1.6 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels, according to the Copernicus Climate Change Service. This alarming increase of 0.1 degrees Celsius from 2023 signifies the first time that global temperatures have surpassed the internationally agreed 1.5-degree Celsius threshold, highlighting the escalating climate crisis. The primary driver of this temperature surge is the combustion of fossil fuels, leading to severe weather patterns and significant harm to millions globally.
Data reveals a record 44% of the Earth’s surface suffered from intense heat stress on 10 July 2024, with 22 July marked as the hottest day ever recorded. The impact of these temperatures has been severe, with increased atmospheric water vapor contributing to unprecedented heatwaves and heavy rainfall, further exacerbating distress for countless individuals. Experts warn that failing to curb emissions could lead to catastrophic heating levels, potentially reaching 2.7 degrees Celsius by century’s end if current practices persist.
As nations prepare for emissions-cutting pledges to the UN in February 2025, the urgency for transformative action to reduce fossil fuel dependency is palpable. Although the natural El Niño phenomenon contributed to temperature spikes in early 2024, the sustained high temperatures in the latter half raise concerns regarding unforeseen factors accelerating climate change. Furthermore, pollution reductions from shipping and decreased low-level clouds have been linked to this rise, warranting further investigation.
The continuous record-breaking temperatures underscore the dire need for extensive emissions reductions. With global warming resulting in more extreme weather events, experts emphasize that even minimal increases in temperature lead to more severe impacts on both human populations and ecosystems.
The issue of climate change has been an escalating concern for global communities and policymakers. Over recent years, rising greenhouse gas emissions, primarily from the use of fossil fuels, have consistently resulted in record-breaking global temperatures. The Paris Agreement set a goal of limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels, aiming for 1.5 degrees Celsius. However, recent data shows that the average global temperature has surpassed this target, prompting significant concern for vulnerable populations and ecosystems worldwide.
The record-high global temperatures in 2024 serve as a critical wake-up call regarding the severity of climate change and its effects on the planet. With temperatures now above the 1.5-degree Celsius threshold, the urgency to transition away from fossil fuels and implement ambitious emissions reductions is paramount. Experts continue to advocate for immediate and concrete policy shifts to halt the trajectory toward catastrophic climate impacts. The situation underscores the necessity for collective action to preserve the environment and secure a sustainable future.
Original Source: www.theguardian.com