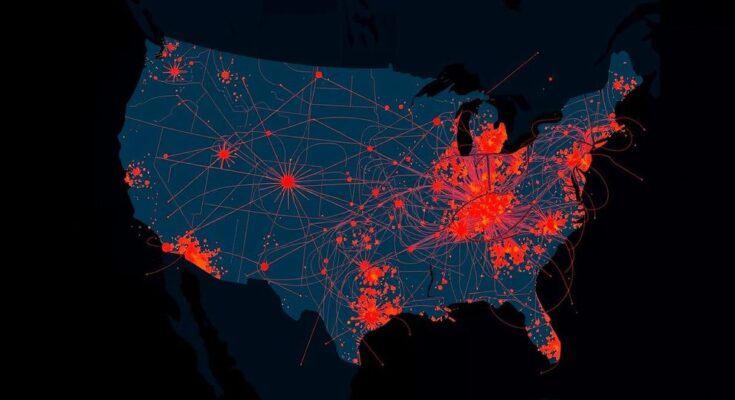
A 4.4-magnitude earthquake struck Borrego Springs, California on November 7, following other significant earthquakes in Greece and Hawaii. The recent seismic activities highlight global geological movements and emphasize the need for awareness and preparedness in earthquake-prone regions.
On November 7, a 4.4-magnitude earthquake occurred in California, specifically centered in Borrego Springs at a depth of approximately 9.8 kilometers. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) recorded 257 instances of residents indicating they felt this earthquake. This seismic event followed a series of notable earthquakes, including a 4.4-magnitude tremor in Greece two days prior, which had a depth of 82.3 kilometers and was centered in Chalandrítsa. Additionally, on the same day as the Greece earthquake, a 4.8-magnitude quake struck Hawaii, centered in Pāhala at a depth of 38.4 kilometers. Notably, hours before the Greece earthquake, a 3.3-magnitude seismic event occurred in California near Anza, at a depth of 12.1 kilometers. Prior seismic activity includes a 4.3-magnitude quake reported in Chile and a 3.7-magnitude earthquake in Missouri on November 5. The Chilean earthquake, centered in La Serena, had a depth of 46.1 kilometers, while the Missouri quake, located in Steele, was recorded at a depth of 10.5 kilometers. Further illustrating this earthquake sequence, a 5.3-magnitude earthquake was reported in Greece on November 3, centered in Néa Poteídaia at a depth of 10.0 kilometers. All of these recent quakes occurred following a significant 6.0-magnitude earthquake in Oregon on October 30, concentrated in Windsor at a depth of 10 kilometers. The seismic activity continued with a 3.2-magnitude quake in California on October 30 and a subsequent 3.2-magnitude earthquake in Lompoc, also recorded shortly after. The series of tremors underscores the persistent seismic activity along the West Coast and beyond, suggesting a need for heightened awareness and preparedness for future events. This report emphasizes the significance of monitoring seismic events as they occur, showcasing the interconnectedness of global earthquake occurrences and the potential for subsequent tremors across various regions.
The recent wave of earthquakes highlights the geological activity prevalent in regions such as California, Greece, Hawaii, and others, underscoring the importance of the USGS in tracking and reporting such seismic events. Understanding earthquake magnitudes, depths, and their geographical locations is crucial for assessing potential impacts on communities and infrastructure. The timing of these earthquakes is particularly relevant as they appear to occur in clusters, indicating active tectonic activity in these regions.
In summary, recent seismic events, including a 4.4-magnitude earthquake in California and notable quakes in Greece and Hawaii, demonstrate the persistent tectonic activities that characterize various geographic regions. It is essential for residents in these areas to remain informed and prepared for future seismic occurrences, as the patterns indicate continued geological instability.
Original Source: koacolorado.iheart.com